A system test is like a health check for your internet connection, ensuring it's reliable and strong enough for seamless communication when using Dialpad. This article goes over the details of the Dialpad System Test and how to understand your results.
Let’s dive into the details.
Who can use this
The System Test is available to all Dialpad users using the Dialpad desktop app and browser app.
How to use the System Test
To launch the System Test, head to your Dialpad app:
Select your avatar
Navigate to Issues during a call
Select System Test
.png)
Confirm your name and email > Select Start a test
Grant audio permissions if prompted
That's it! You'll soon have detailed results.
Test components
The System Test is an easy, yet powerful, way to test your connection when you encounter poor audio quality.
Specifically, it checks the following call components:
Network Score
Throughput
Call Quality
Location
Bandwidth Speed
DNS Look Up
Device State
Machine Information
Turn Connectivity
Ping
Video Bandwidth
Only visible when testing video quality ( Dialpad Meetings).
From the test results menu, you can view logs, copy the ID, download the results as a PDF, or change the language.
You can also view the logs for each component individually.
.png)
Let's look at each test component.
Network Score
The Network Score provides a simple summary score that shows how effectively your device and network can manage voice communications. The score is generated using data from the Throughput, Call Quality, and Bandwidth
Speed widgets help you quickly understand your network's readiness without needing in-depth knowledge of complex VoIP metrics.
What to look for
The higher the score, the better. If you receive poor scores, review the logs from the Throughput, Call Quality, and Bandwidth Speed widgets to better understand the issues.
Throughput
Throughput is the number of packets sent successfully from one place to another. The Throughput Test checks the amount of data that your network can send and receive at the same time. This test sends 1 KB of data every second over your network and measures the rate they are received.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
Maximum: The highest throughput measured throughout the test.
Average: The average throughput achieved during the test.
Minimum: The lowest throughput recorded throughout the test.
What to look for
Low minimum throughput and high variance between the minimum, average, and maximum may indicate your connection is unstable and jittery.
Call quality
The Call Quality Test verifies the quality of your video and audio calls.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
Mean Opinion Score (MOS): An industry-wide standard measure of call quality.
Learn more about the MOS scale in this Help Center article.
A higher score indicates a higher-quality call.
Round Trip: The time it takes for a packet to be sent and a reply to be received back
A smaller number means better call quality.
Packet Loss: The number of packets lost during the test.
A lower number means you have higher call quality.
A higher number may result in choppy audio.
Jitter: The inconsistent delivery of data packets over your internet connection.
A lower number means better call quality.
A higher number may result in voice or video distortion.
What to look for
You’re looking for a high MOS score and low jitter, packet loss, and round-trip values.
Optimal values
Jitter: Less than 40 milliseconds
Packet Loss: Less than 2%
Latency: Less than 125 milliseconds
Acceptable values
Jitter: Less than 100 milliseconds
Packet Loss: Less than 5%
Latency: Less than 200 milliseconds
There are also environmental factors that can play into this which is typically described as sounding like “in a tunnel” or “in a cave” which is due to an echo with delay. Put simply not using a headset, in a room with hard walls the audio from the speakers hit the wall, echo back and are picked up by the microphone.
You'll also see call quality details listed in the Call Summary. The Quality section provides insight into bitrate, packet loss, jitter, and latency..png)
If you see high numbers or experience varied call quality, we recommend running the System Test to troubleshoot.
Location
The Location Test checks your location based on your public IP address and browser. Location is important because the farther you are from a server, the higher the chance of an issue.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
IP Address: A unique ID that identifies a specific device connected to a network.
This is where the network test sees where the request is coming from.
City: Using an external identification service, we estimate your city based on your IP address
Accuracy ranges from 50-70%.
Country: Using an external identification service, we identify your country.
Accuracy ranges from 95-99%.
Organization: The provider who owns the IP address.
Note
Depending on your subscription, the Location report logs might provide extra IP details.
Signaling and media location
Your location results may show two different IP addresses: one for HTTPS and the other for real-time media. This usually happens when:
A VPN is active and splits your signaling and media location into two.
Remember, Dialpad does not support VPNs.
An IPv6 is used for signaling, but the media server only supports IPv4.
Having two different IP addresses doesn't always mean there's a problem. However, if there are problems, having two separate IP addresses could help us figure out why they're happening.
Bandwidth Speed
The Bandwidth Speed Test checks how quickly data can be transmitted over a network connection.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
Best Region: The most optimal data center for your test (identified through your IP address and latency, and the available servers)
Uplink: The speed at which your connection can send information to the server.
Downlink: The speed your connection can receive information from the server.
Jitter: The amount of data that is stuck on the way to the server, usually because of congestion.
The lower the Jitter, the better.
What to look for
Higher bandwidth means that your data can be transferred faster, resulting in better-quality audio and video.
A higher uplink and downlink indicates better network conditions. The Bandwidth Speed test only assesses the maximum data capacity of your connection.
If you can't connect, your network likely cannot reach the testing server due to firewall restrictions.
DNS lookup
The DNS Lookup checks your connection to HTTPS and WSS addresses. If DNS servers are inaccessible, parts of your service may be unavailable.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
Connected: The number of successfully connected addresses out of the total number attempted.
Average Connection Time: The average time it took to connect to the servers.
Highest Connection Time: The maximum time it took to connect with one of the servers.
Shortest Connection Time: The fastest time it took to connect with one of the servers.
What to look for
High connection times can indicate a routing issue, and if any of the addresses are unreachable, Dialpad will likely not work.
A blocked DNS address means that the DNS address could not be reached within 5 seconds.
If your DNS is blocked, check your firewall and whitelist rules with your IT team.
Device state
The Device State Test collects valuable information about your device. This is helpful when troubleshooting another person’s connection.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
Audio: Shows device mic and speaker detected during the test.
Device: Displays the name of the connected audio device.
Network: Shows what network your browser thinks it is connected to.
Connection tip
WiFi connections are convenient but can have ‘dead’ spots. Use a wired internet connection for optimal service. Read this Help Center article for tips on troubleshooting your home network.
Machine information
The Machine Information Test displays detailed insights about your machine, including CPU usage, battery level, available memory, and more.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
CPU Usage: Shows the percentage of CPU being used.
Memory: Displays how much memory your device is using, and how much is available.
Battery: Shows battery level and charging status.
Model: The type of processor your device uses.
Storage: Displays how much storage your device offers.
OS: Displays the type of operating system your device uses.
Turn connectivity
The Turn Connectivity Test displays the time it takes a connection to be established between the machine being tested and the TURN server — this is particularly important for real-time communication applications like voice calls, video conferencing, where low latency and high reliability are crucial.
TURN connectivity ensures that communication can still occur even when direct connections are blocked or not possible due to network configurations.
This component of the System Test collects the following information:
User Datagram Protocol (UDP):A communications protocol for time-sensitive applications like gaming, playing videos, or Domain Name System (DNS) lookups.
UDP results in speedier communication because it does not spend time forming a firm connection with the destination before transferring the data.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): A standard for delivering data and messages over networks. It's a common protocol used in digital network communications.
Transport Layer Security (TLS): Encrypts data sent over the Internet to ensure that eavesdroppers and hackers are unable to see what you transmit which is particularly useful for private and sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal correspondence.
For the purpose of TURN, TLS isn’t used for encryption (since WebRTC already encrypts the data between the peers) but rather to try and get around firewalls which only allow for TLS encrypted communications to pass through.
The values for UDP, TCP, and TLS in the widget indicate the time it has taken for a connection to be established between the machine being tested and the TURN server.
This number includes the time taken to:
Gather the candidate
Connect to it
Negotiate any necessary certificates
What to look for
If UDP is blocked and marked with a red X, your sessions either don’t connect at all or will be degraded by the use of TCP or TLS. It is highly recommended that your network be open for UDP traffic and configured properly to be reachable for live media exchange.
The number does not indicate latency or roundtrip—only the initial connection time. For actual network latencies, it is best to look at other tests conducted for their RTT (roundtrip time) measurements.
Ping
The Ping Test measures the HTTP round-trip time to determine the closest viable data center.
This test gives a general indication of the distance between your location and the various data centers you operate.
What to look for
The lower the number, the better! A lower ping number indicates better network performance and faster response times.
Video Bandwidth
The Video Bandwidth Test checks the video throughput bandwidth to give a general indication of the available send bandwidth.
This test is conducted by running a real video call relayed through a TURN server, and collects the following information:
Incoming and outgoing quality metrics.
Network type of connection.
Type of connection (direct or routed; over UDP, TCP or TLS).
IP+port pair of the connection established.
What to look for
The higher the bandwidth, the better quality your video calls will be.
Bandwidth requirements vary depending on the type of video call you're having.
Video 1:1 Calls: minimum of 1.2-1.5Mbps up/down
Video Meetings: minimum 1.2-1.5Mbps up and 3Mbps down
Mobile Video (any): 4G+ (or equivalent wifi access)
Frequently asked questions
Can I send a copy of the report to another person?
Yes! Select Download as PDF to save a copy of your report. Once downloaded, you can send it to anyone. 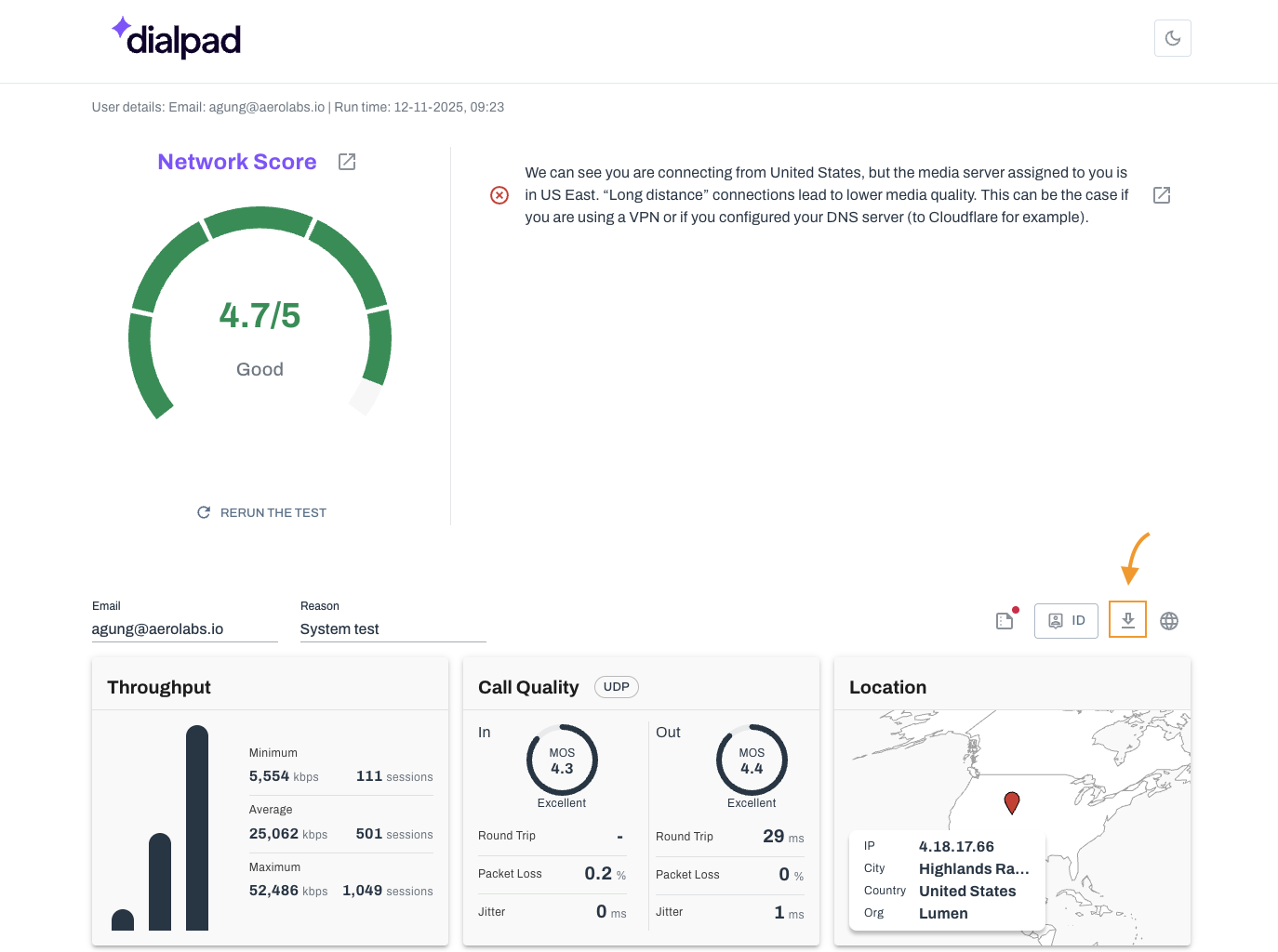
Why don't I see this option on my mobile?
The System Test is only available on the Dialpad desktop app and browser app.
My score was low, what do I do?
If your score was low, first things first, review the recommendations provided at the top of the test.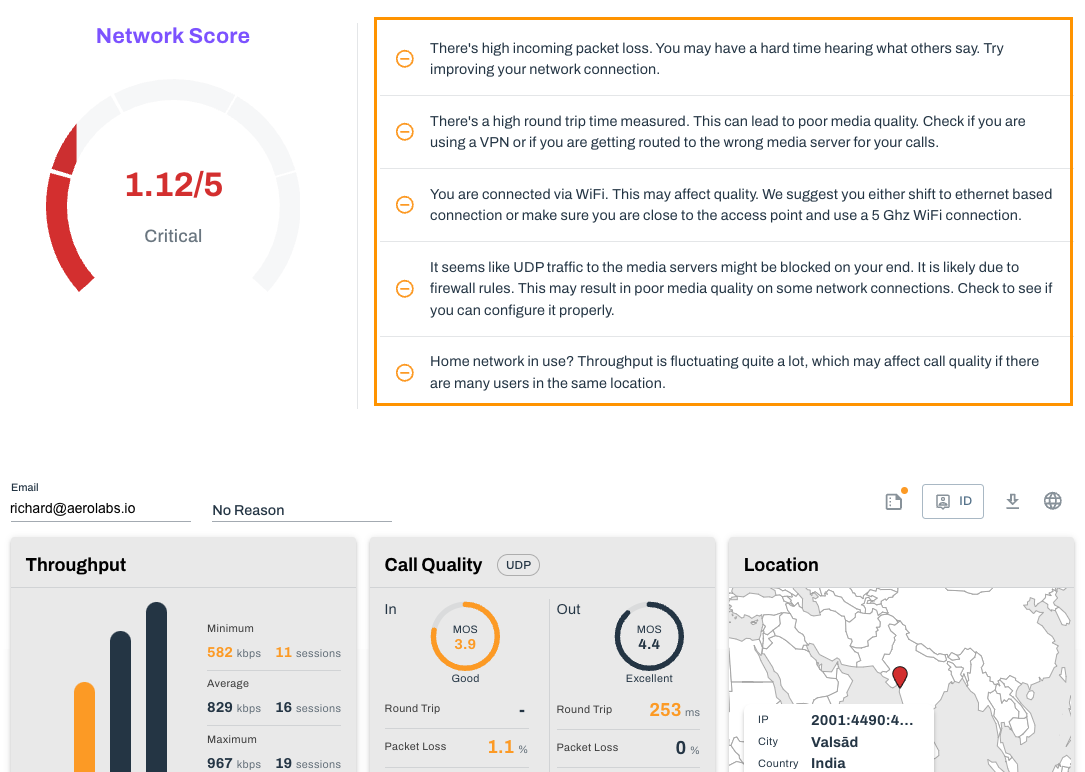
Once you've made the suggestions, run the System Test again.
If you continue to experience issues, check with your IT Team, or reach out to Dialpad's Customer Care Team.