A big part of planning a customer support team is understanding the impact of shrinkage. Shrinkage is the time when team members aren’t available to take calls or help with customer-related tasks.
Shrinkage can happen for many reasons, and it’s important to factor it in when planning the number of agents needed to handle call volumes effectively.
Let’s dive into the details.
Types of Shrinkage
There are two types of shrinkage, external and internal.
External shrinkage - Includes factors beyond your control, like vacations, public holidays, or unexpected sick days.
Internal shrinkage - Includes team-controlled factors, such as time agents spend away from queues for breaks, meetings, training, and offline tasks like admin work.
Download External Shrinkage
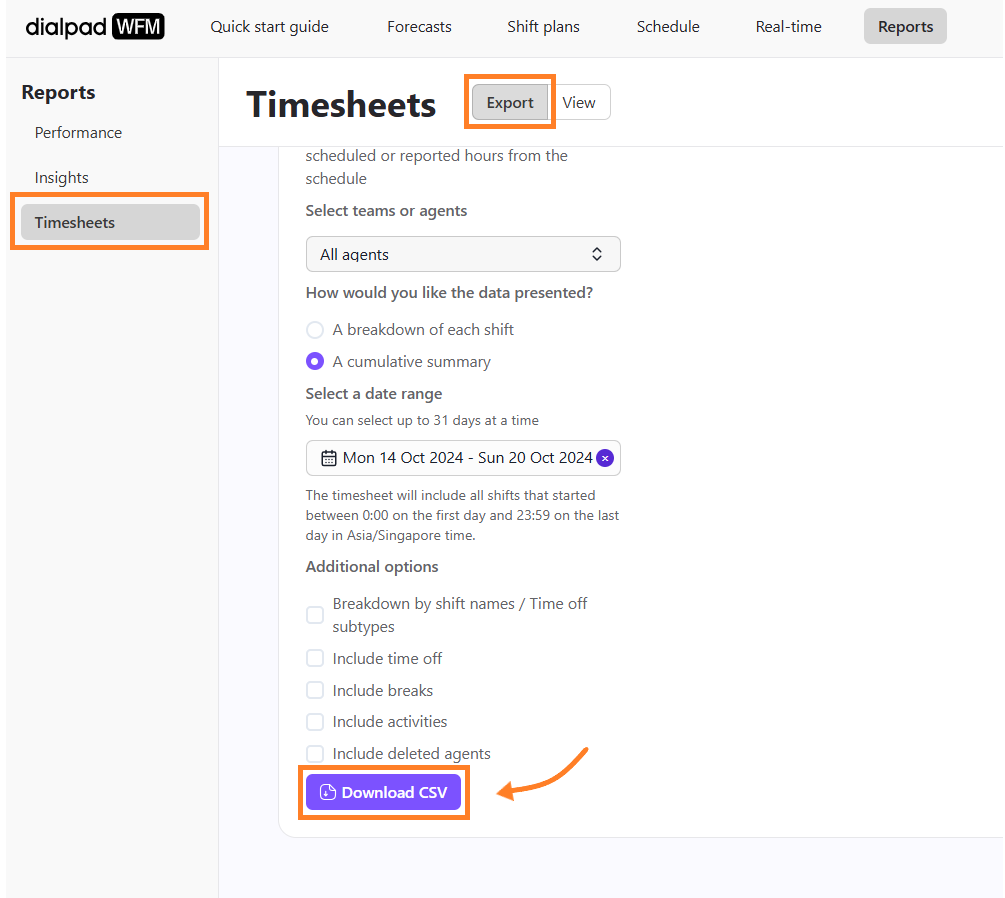
To download data on your team’s external shrinkage, head to Dialpad WFM and navigate to Reports.
Select Timesheets
Select Export
Navigate to Select teams or agents
Select A cumulative summary
Filter the date range
Navigate to Additional options
Check the box beside Breakdown by shift names/time off subtypes
Check the box beside Include time of
.png)
Select Download CSV
View internal shrinkage
Your team’s internal shrinkage can be viewed on:
The Performance page
The Insights page
Let's look at each.
See shrinkage from the Performance page
To get the shrinkage data on the Performance page, head to Dialpad WFM and navigate to Reports.
Select Performance
Filter the date range
.png)
Select the teams and/or agents
Then, take the inverse of the Utilization figure to calculate the internal shrinkage amount.
In the sample above, the internal shrinkage is 32%.
Note
To account for time lost due to non-adherence in your shrinkage report, add the inverse of the Time-on-Task to the non-utilized time shrinkage.
For example, in the sample above, the combined internal shrinkage is 38.5%. (32% of non-utilised time + 6.5% of time spent out off-task)
See shrinkage from the Insights page
To get the shrinkage data on the Insights page, head to Dialpad WFM and navigate to Reports.
Select Insights
Filter the date range

Select the teams and/or agents
Navigate to the Queue and Offline activities breakdown. The Insight card on the right shows the percentage of agent time spent on queue activities for the date range. The inverse of this percentage is your internal shrinkage data — e.g., 42.6% in the example above.
Note
The Offline Activities section shows the percentage of each activity that contributes to your overall internal shrinkage, providing a detailed breakdown.
Total working hours
Know your team’s total working hours before calculating shrinkage.
You can download your agent’s working hours, head to Dialpad WFM, and go to Reports.
Select Timesheets
Select Export
Select the teams and/or agents
Select A cumulative summary
Filter the date range to weekly
Select Download CSV
To calculate your team’s total contracted hours per week, sum the values in the weekly_contract_hours column and divide by the number of agents. You can then add this calculation for longer periods.
Example
You have 100 agents who work 40 hours a week. Over a 4-week month, that works out to 1600h.
Calculate total shrinkage
To calculate your total shrinkage, you’ll need these three values.
Total contracted hours
External shrinkage %
Internal shrinkage %
Then, add your external and internal shrinkage percentages to get the total shrinkage value for the selected agents and period.
Example
4.5% (external shrinkage) + 50.2% (combined internal shrinkage) = 54.7% total shrinkage.
If your team works 4500 hours a month, and your total shrinkage is 54.7% then you are losing 2461 hours a month from productive queue time.
Tip
Some teams find it helpful to express shrinkage based on one full-time agent to show the value of hiring and staffing to reduce shrinkage.
For example, if a full-time agent works 173 hours a month, and your total shrinkage is 54.7% then that agent loses 94 hours a month to un-productive queue time. This means you only get 79 hours of queue time for each full-time agent hired or staffed.
Calculate Shrinkage per queue
When creating your queues, you’ll be asked to enter a shrinkage percentage to ensure your staffing plans account for the time agents spend away from the queue.
Note
You can use the same percentage for all queues, or create a specific percentage for each queue.
To get the shrinkage data per queue, head to Dialpad WFM and go to Reports.
Select Performance
Filter date range
Select the teams and/or agents
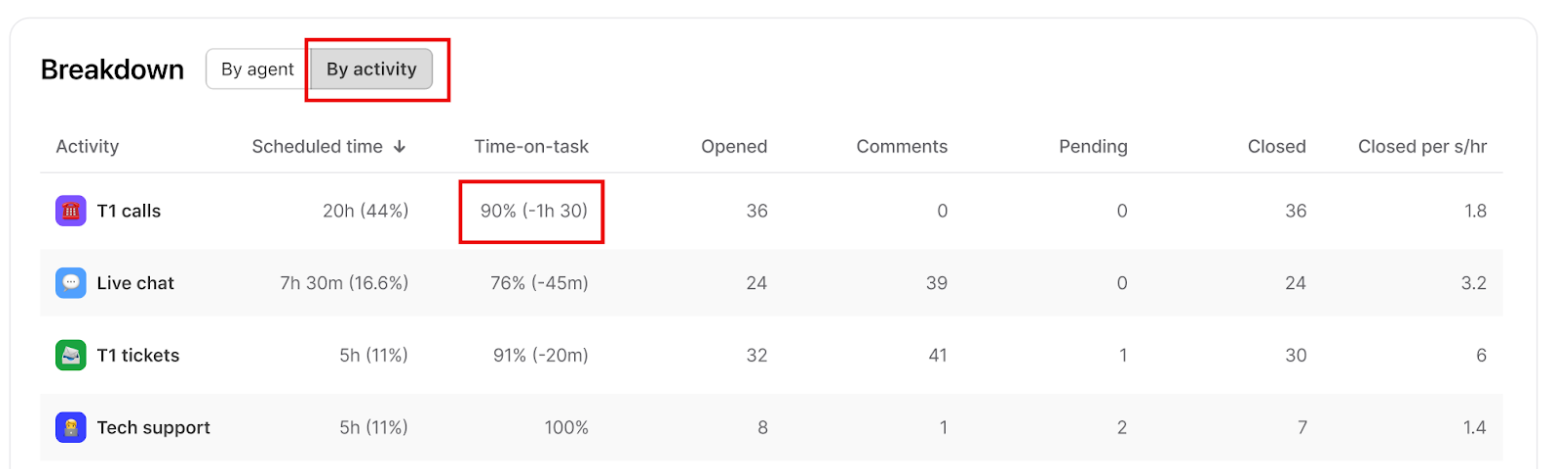
In the Breakdown table, select the By activity view and find the activities linked to that queue.
To calculate shrinkage for a queue, take the inverse value of Time-on-task and add the non-utilized time. The result will give you the queue's shrinkage.
Example
Based on the sample below, your non-utilized time is 35.9% + 10% spent off-task for the T1 calls queue. This means the total internal shrinkage for this queue is 45.9%.
(1).png)
.png)